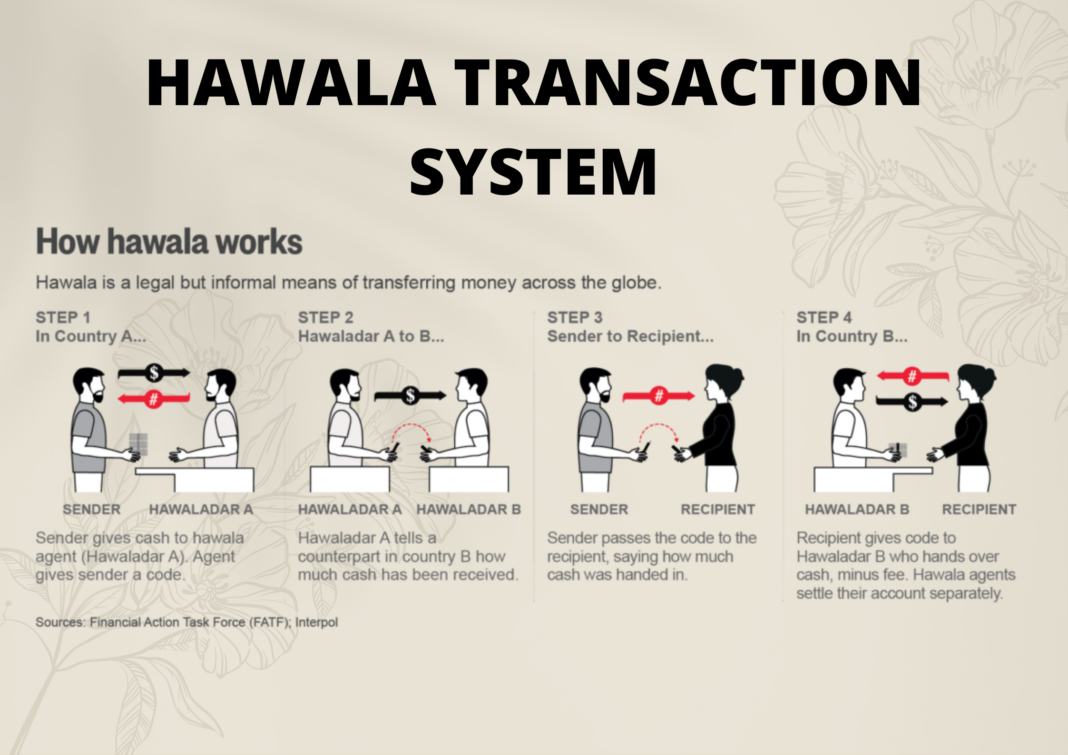
The word “Hawala” means trust. It is an alternative or parallel remittance system, which works outside the purview of regulations.
Hawala is an ancient system of money transfer that originated in South Asia and is now being used across the globe. This was created centuries ago in India and China before Western financial systems were established to facilitate the secure and convenient movement of funds.
Merchant traders wishing to send funds to their homelands would deposit them with a hawala broker or hawaladar who normally owned a trading business. For a small fee, the hawaladar would arrange for the funds to be made available for withdrawal from another hawaladar, normally also a trader, in another country.
It is also sometimes referred to as “Underground Banking”. Though it is being used across the world to remit funds, it is not a legal system.
It works on the basis of many middlemen called the hawaldars or the hawala dealers. The reason, why Hawala is extensively used in spite of the fact that it is illegal, is the inseparable element of trust and extensive use of family or regional affiliations.
Alternate Names for Hawala
Hawala is known by different names in India. There is a history of this in two Indian states viz. Kerala and Gujrat. In the migrant population of the middle-eastern states if the ethnicity is analyzed then you find most Indians coming from these two states. In the state of Kerala Hawala is also termed as Tube Money or Pipe Money. Pipe money refers to illegal, transfer of foreign exchange into the country hiding from the government. So in the local Malayalam Language, it is called Kuzhalpanam.
Additionally, Angadia system is a century-old parallel banking system in India. in this, traders send cash from one state to another through a person called Angadia. This system is quite popular among the citizens of Kerala and Gujrat. Angadia stands for courier.
How Does Hawala Work?
Hawala works by transferring money without actually moving it. In a this type of transaction, no physical movement of cash is there. This system works with a network of operators called Hawaldars or Hawala Dealers.
A person who is willing to transfer money contacts a this operator at the source location. The operator at that end collects the money from that person who wishes to make a transfer. He then calls upon his counterpart or the other operator at the destination place/country was the transfer has to be made.
Now the hawala operator at the transferee’s end hands over the cash to the intended recipient after deducting a certain amount of commission.
Example of Hawala Transaction
The best way to understand Hawala is through understanding a single hawala transaction. For example, Abraham, a Kerala Resident, is a taxi driver staying in UAE. He wants to remit some money to his family in India. Abraham cannot approach a bank as there are numerous restrictions on opening a bank account in a foreign country.
Thus, Abraham finally lands up at a hawala operator’s office, who not only promises him to deliver the cash to his native place in India at a reasonable commission but also in a very short period of time. Abraham then hands over the cash to Khan, A Hawala operator. The Khan then calls his Indian counterpart and asks him to deliver funds to Abraham’s house in Kerala.
After the deduction of commission charges and producing an authentication code, which is generally used in all hawala transactions, cash is handed over.
Reverse Hawala
A reverse Hawala transaction can also be initiated, where a father approaches the same Indian hawala operator for remitting funds for his son studying in the UAE through Khan who is a hawala operator. In this manner, money never actually moves. The position of the hawala operators in each other’s books gets squared off.
Is Hawala Illegal?
Hawala has been made illegal in many countries, as it is seen to be a form of money laundering and can be used to move wealth anonymously. As these transactions are not routed through banks they cannot be regulated by government agencies and have thus emerged as a major cause of concern.
Hawala gained prominence when the investigations into 9/11 revealed that the money was paid to the terrorists through informal remittance systems.
This network is being used extensively across the globe to circulate black money and to provide funds for terrorism, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities. In India, FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) 2000 and PMLA ( Prevention of Money Laundering Act) 2002 are the two major legislations that make such transactions illegal.
White Hawala
White hawala occurs when the transaction is with legitimate funds and is seemingly harmless when someone sends money to a relative. Black hawala deals in transactions where the funds are illegitimately derived from major criminal activity such as drug or human trafficking or used for criminal purposes money laundering or terrorist financing.
Why do people still use Hawala?
In spite of the fact that hawala transactions are illegal, people use this method because of the following reasons:
- The commission rates for transferring money through hawala are quite low
- No requirement of any id proof and disclosure of the source of income is there
- It has emerged as a reliable and efficient system of remittance
- As there is no physical movement of cash, hawala operators provide better exchange rates as compared to the official exchange rates
- It is a simple and hassle-free process when compared to the extensive documentation being done by the banks
- It is the only way to transfer unaccounted income
So, the next time you come across the word Hawala, I am sure you will be able to draw a picture of the transaction in your mind.
Hawala Settlements
Typically, Hawala brokers or Hawaldars our business partners engaged in the import and export of goods. They may be engaged in illegal transfers of goods like drugs or precious gems and jewelry.
To move goods illegally they would print an invoice with lesser money than the actual value. When a hawala operator pays a recipient, he might be actually paying off the debts owned by him to the operator.
Apart from business settlements, rarely, the funding can be from illegal means as an effort to launder money. The back payment between the hawala brokers can happen as a counter hawala transaction as well.
The hawala agents keep a tally of the money that they owe to each other. Once the settlement is done, they don’t keep any record of that transaction, making the hawala very difficult to trace.